Generative AI is a form of artificial intelligence (AI) that leverages algorithms and neural networks to create new and original content, including text, images, audio, synthetic data, and other media.
Generative AI creates new, realistic content using raw data from existing NLP machine learning models and algorithms. It generates outputs in response to specific prompts based on the patterns and structures it identifies within the data it’s trained on.
Generative AI models, having been trained on massive data sets through deep learning and deep neural networks, can engage in conversations, respond to inquiries, author stories, generate source code, and conjure images and videos tailored to any description—all initiated by concise text inputs or “prompts.”
Research from McKinsey highlights that generative AI could add between $2.6 trillion and $4.4 trillion in value to the world’s economy by improving productivity.
So it’s no wonder this term has been creating a stir in the tech world, mainly due to the escalating popularity of generative AI applications such as OpenAI’s conversational assistant ChatGPT and the AI image creator DALL-E.
This article will explore the many facets of generative AI and its many applications.
By the end of this article, you will know:
- Understanding Generative AI and Its Mechanisms
- Benefits of Generative AI for Businesses
- Diverse Applications of Generative AI
- Prime Examples of Generative AI Models
- Limitations of Generative AI
- Risks in Implementing Generative AI
- Generative AI’s Role in Digital Adoption
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI relates to artificial intelligence systems that forge human-resembling content—images, videos, music, and text—from the ground up.
Predominantly, generative AI finds its application in large language models (LLMs), utilizing deep learning algorithms to scrutinize extensive textual data.
This enables them to comprehend the structure of human language and to produce unique content ‘inspired’ by the original sources it has analyzed.
Why Is Generative AI Important?
Generative AI is important due to its transformative potential in various domains.
Here’s why:
- Content Creation: It can produce original content like articles, music, and images, thereby automating and streamlining the creative process.
- Data Augmentation: Generative AI can create synthetic data for training machine learning models, especially when real data is scarce or sensitive.
- Personalization: It can customize content based on individual preferences, enhancing user experience in areas like eCommerce, marketing, and entertainment.
- Simulation: In industries like automotive and aerospace, generative AI can simulate different scenarios for testing and validation, reducing costs and risks.
- Innovation: By generating new ideas, designs, and strategies, it can drive innovation across sectors.
However, it’s crucial to use generative AI responsibly due to potential risks such as deepfakes and misuse of synthetic data. Despite these challenges, the benefits of generative AI make it an essential tool in the digital age.
How Does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI starts with a prompt, which can take various forms such as text, image, video, design, or musical notes—essentially any input the AI system can interpret.
After this, different AI algorithms generate new content in reaction to the prompt, which may encompass essays, problem solutions, or convincing forgeries crafted from an individual’s pictures or audio.
Innovators in generative AI are cultivating enhanced user experiences, enabling users to articulate requests in straightforward language.
After receiving an initial response, users can fine-tune the results, offering human feedback regarding the style, tone, and other aspects they desire to be reflected in the generated content.
What Are The Benefits Of Generative AI?

Although generative AI may not yet be able to replace humans fully, it does enhance the capabilities of your employees, assisting them in automating monotonous, repetitive tasks, managing and validating substantial data volumes, and addressing recurring queries and tickets.
Here are some advantages you might anticipate upon integrating generative AI into your organization:
- Facilitating the automation of manual content writing processes.
- Diminishing the efforts required to respond to emails.
- Enhancing the addressing of specific technical inquiries.
- Generating lifelike portrayals of individuals.
- Condensing complex data into a straightforward, comprehensible narrative.
- Streamlining the creation of content adhering to a particular style.
- Personalizing the customer experience.
Use Cases For Generative AI
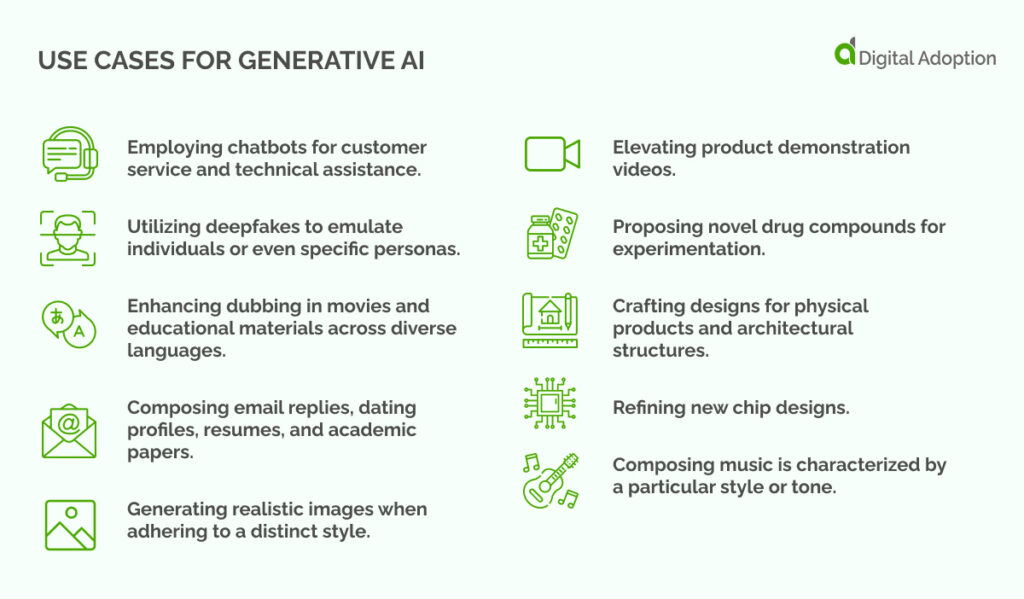
Generative AI can be utilized across numerous scenarios to create almost any type of content.
Some of the practical applications for generative AI are:
- Employing chatbots for customer service and technical assistance.
- Utilizing deepfakes to emulate individuals or even specific personas.
- Enhancing dubbing in movies and educational materials across diverse languages.
- Composing email replies, dating profiles, resumes, and academic papers.
- Generating realistic images when adhering to a distinct style.
- Elevating product demonstration videos.
- Proposing novel drug compounds for experimentation.
- Crafting designs for physical products and architectural structures.
- Refining new chip designs.
- Composing music is characterized by a particular style or tone.
What Are The Best Examples Of Generative AI Tools?

Some of the renowned generative AI tools include:
- GPT, Jasper, AI-Writer, and Lex to generate text.
- Explore Dall-E 2, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion for image generation.
- Consider Amper, Dadabots, and MuseNet in the realm of music generation.
- CodeStarter, Codex, GitHub Copilot, and Tabnine are worthwhile to create code.
- Descript, Listnr, and Podcast.ai are available for voice synthesis.
- Companies like Synopsys, Cadence, Google, and Nvidia are prominent in AI chip design.
The Impact of ChatGPT on Generative AI
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, has had a profound impact on the field of generative AI.
As a large-scale, language-based model, it has demonstrated remarkable proficiency in generating human-like text.
Here’s its impact:
- Benchmark for Quality: ChatGPT’s ability to understand context and generate coherent responses has set a high standard for AI-generated text quality.
- Versatility: It’s used in various applications, from drafting emails to writing code, showcasing the versatility of generative AI.
- Accessibility: It has made generative AI more accessible to non-technical users, encouraging widespread adoption.
- Research Advancements: The success of ChatGPT has spurred further research in AI, pushing the boundaries of what generative models can achieve.
Despite concerns over misuse, ChatGPT’s impact underscores the transformative potential of generative AI in communication, productivity, and beyond.
Limitations Of Generative AI
While generative AI holds transformative potential, it grapples with significant limitations, including accuracy issues and the potential propagation of misinformation.
Here are the limitations of generative AI:
- Generative AI models process vast amounts of internet content to make predictions and generate outputs based on prompts.
- The accuracy of these responses is not guaranteed, despite seeming plausible.
- Responses may reflect biases from the model’s training data, with no clear method to determine this.
- The role of generative AI in spreading misinformation has raised significant concerns due to these factors.
- These models lack the ability to verify the accuracy of their generated content.
- We often have little insight into the source of the information and how algorithms manipulate it to produce content.
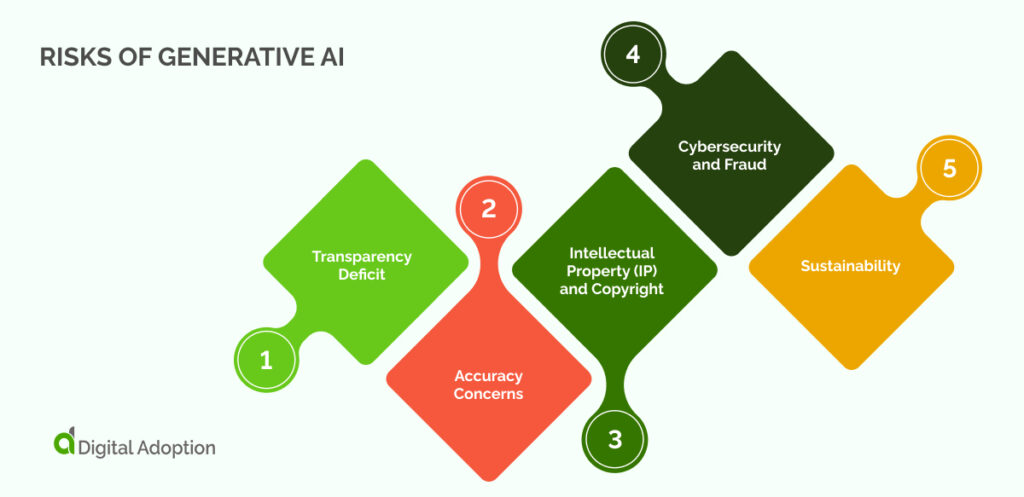
Risks Of Generative AI
ChatGPT and similar tools are trained on extensive quantities of publicly accessible data.
They are not engineered to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other copyright laws, hence the critical importance of meticulously monitoring your enterprise’s utilization of these platforms.
Important risks worth scrutinizing in terms of generative AI include:
Transparency Deficit
Generative AI and ChatGPT models exhibit unpredictability; even the entities that developed them might not fully comprehend their functionality. These models need to be trained on fuller, diverse datasets.
Accuracy Concerns
Generative AI systems can occasionally generate inaccurate or entirely fabricated answers. Evaluating all outputs for accuracy, relevance, and utility is essential before relying on or disseminating information.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Copyright
There are no confirmable data governance and protection guarantees concerning confidential enterprise data.
Users should assume that any data or queries submitted into ChatGPT and its counterparts might become public information. Enterprises should establish controls to prevent accidental exposure to IP.
Cybersecurity and Fraud
Enterprises should brace for the possibility of malevolent actors using generative AI systems for cyber and fraud attacks, such as deploying deep fakes for social engineering schemes targeting personnel, and ensure that counteractive controls are established.
Engage with your cyber-insurance provider to ascertain the extent to which your existing policy envelops AI-related breaches.
Additionally, data shared with a generative AI-powered chatbot could be unintentionally shared with third parties, advancing breaches or violations.
Sustainability
Generative AI consumes substantial electrical power. Opt for vendors that minimize power usage and employ high-quality renewable energy to diminish the impact on your sustainability objectives.
Can Generative AI Help With Digital Adoption?
Large machine learning models are at the core of developing artificial intelligence that aids users in adopting business software.
A digital adoption platform can enhance the customization of predictions and recommendations for each individual user by training the AI system with user-specific data.
This AI-powered digital adoption platform provides real-time interactive guidance, proactive action tips, intelligent reminders, and automated user support directly within their applications.
Generative AI-powered self-help features can minimize users’ time accessing personalized knowledge base articles, external links, and other documentation.
Generative AI can also help organizations track, visualize, and analyze applications, software processes, and data pertinent to enterprise-level digital adoption.
This data is vital for IT and business leaders to understand software license usage, adoption, and engagement metrics for all mission-critical applications. Through data analysis, enterprises can obliterate productivity impediments and foster enhanced efficiency.
What’s Next For Generative AI?
As we navigate the frontier of artificial intelligence, the next phase for generative AI promises a future of enhanced productivity, improved communication, streamlined business processes, and rapid advancements in sectors like automotive design.
These are our data-driven predictions on what’s next for generative AI:
- Labor Productivity Boost: Generative AI can automate routine tasks and processes, freeing human workers to focus on more strategic, higher-value activities. This could lead to significant increases in productivity across various sectors, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. The economic benefits could be substantial, contributing to growth and competitiveness.
- Interactive AI: The evolution of generative AI could result in interactive AI systems that can carry out complex tasks set by users. These systems could collaborate with other software and humans, leading to more efficient workflows and problem-solving capabilities. For example, an interactive AI system could help manage a project by coordinating tasks among team members and tracking progress.
- Real-time Translation and Audio Dubbing: Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize communication and entertainment sectors with applications like real-time translation and audio dubbing. Imagine watching a foreign film with real-time dubbed voiceovers in your language, made possible by generative AI.
- Automated Summarization: With the vast amounts of data generated today, businesses need efficient ways to digest and understand it. Generative AI could automatically summarize complex information, making it easier for decision-makers to gain insights and make informed decisions. For instance, a news organization could use generative AI to create concise summaries of long reports or articles.
- Enterprise Automation: Businesses are always looking for ways to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Generative AI could automate more processes, from customer support to supply chain management. By handling routine tasks, organizations could achieve more with fewer resources, potentially opening up new business opportunities as costs decrease.
- Automotive Design: Generative AI is set to disrupt the automotive industry by speeding up the design process. It could transform simple sketches into detailed 3D designs, reducing the time it takes to prototype new vehicle models. This could lead to faster innovation cycles and more creative design possibilities.
- Rapid Development: The field of generative AI is advancing rapidly. Just as we’ve seen significant progress from GPT-2 to ChatGPT within two years, we can expect similar leaps in the capabilities of generative AI systems in the near future. These advancements could unlock new applications and use cases that we can’t even imagine today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is generative AI the same as machine learning?
Machine learning is a subdivision of AI that instructs a system to formulate predictions by leveraging the data it has been trained on. For instance, DALL-E can generate an image in response to a given prompt by interpreting the underlying meaning of that prompt.
Thus, while generative AI is a machine-learning framework, it’s essential to note that not all machine-learning frameworks qualify as generative AI.
What are generative AI systems?
Generative AI, although a topic of discussion for years and arguably since the development of ELIZA (a chatbot simulating a therapist) at MIT in 1966, has recently witnessed a blossoming of innovations as a result of progress made in terms of AI and machine learning.
ChatGPT, known for its strikingly human-like text generation, is almost certainly on your radar. DALL-E and Stable Diffusion have also garnered attention for their capabilities to generate vivid and lifelike images from textual prompts.
Moreover, Google has introduced an enhanced version of Bard, utilizing its most advanced Large Language Model, PaLM 2, enabling Bard to respond to user queries.













